Introduction to AI Agents
Agents are revolutionizing the way we approach complex tasks, leveraging the power of large language models (LLMs) to work on our behalf and achieve remarkable results. In this guide we will dive into the fundamentals of AI agents, exploring their capabilities, design patterns, and potential applications.
What is an Agent?
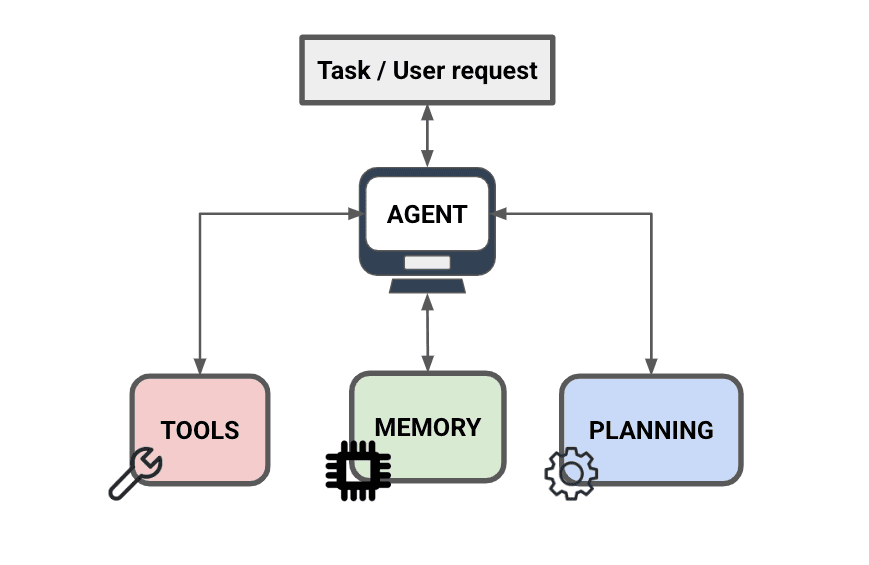
In this guide, we refer to an agent as an LLM-powered system designed to take actions and solve complex tasks autonomously. Unlike traditional LLMs, AI agents go beyond simple text generation. They are equipped with additional capabilities, including:
- Planning and reflection: AI agents can analyze a problem, break it down into steps, and adjust their approach based on new information.
- Tool access: They can interact with external tools and resources, such as databases, APIs, and software applications, to gather information and execute actions.
- Memory: AI agents can store and retrieve information, allowing them to learn from past experiences and make more informed decisions.
This lecture discusses the concept of AI agents and their significance in the realm of artificial intelligence.
Why build with Agents?
While large language models (LLMs) excel at simple, narrow tasks like translation or email generation, they fall short when dealing with complex, broader tasks that require multiple steps, planning, and reasoning. These complex tasks often necessitate access to external tools and information beyond the LLM's knowledge base.
For example, developing a marketing strategy might involve researching competitors, analyzing market trends, and accessing company-specific data. These actions necessitate real-world information, the latest insights, and internal company data, which a standalone LLM might not have access to.
AI agents bridge this gap by combining the capabilities of LLMs with additional features such as memory, planning, and external tools.
By leveraging these abilities, AI agents can effectively tackle complex tasks like:
- Developing marketing strategies
- Planning events
- Providing customer support
Learn how to build with AI agents in our new course. Join now! (opens in a new tab) Use code PROMPTING20 to get an extra 20% off.
Common Use Cases for AI Agents
Here is a non-exhaustive list of common use cases where agents are being applied in the industry:
- Recommendation systems: Personalizing suggestions for products, services, or content.
- Customer support systems: Handling inquiries, resolving issues, and providing assistance.
- Research: Conducting in-depth investigations across various domains, such as legal, finance, and health.
- E-commerce applications: Facilitating online shopping experiences, managing orders, and providing personalized recommendations.
- Booking: Assisting with travel arrangements and event planning.
- Reporting: Analyzing vast amounts of data and generating comprehensive reports.
- Financial analysis: Analyzing market trends, assess financial data, and generate reports with unprecedented speed and accuracy.